
It is one of the variances which company need to monitor beside direct material usage variance. Angro Limited, a single product American company, employs a proper standard costing system. The normal wastage and inefficiencies are taken into account while setting direct materials price and quantity standards. Variances are calculated and reported at regular intervals to ensure the quick remedial actions against any unfavorable occurrence.
- In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $6.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity used is 0.25 pounds.
- Standard variances are considered a red flag for management to investigate and determine their cause.
- In this case, the actual quantity of materials used is \(0.50\) pounds, the standard price per unit of materials is \(\$7.00\), and the standard quantity used is \(0.25\) pounds.
What is your current financial priority?
Standards are cost or revenue targets used to make financial projections and evaluate performance. For example, if the cost formula for supplies is $3 per unit ($3Q), it is also considered the standard cost for supplies. Managers can use the standard cost formula to make projections direct materials variance formula about supplies expense or to evaluate the actual amount spent on supplies. The material yield variance for March was favorable because company actually produced 32,340 tons of output which was higher than the standard output of 31,000 tons based on input quantity of 34,100 tons.
Possible Causes of Direct Materials Variances
However, manufacturing costs were higher than expected at the end of the period. Accordingly, Patty decided to perform a standard cost variance analysis on the variable manufacturing costs. The left side of the DMPV formula estimates what the actual quantity of direct materials purchased should cost according to the standard price allowed in the budget. The right side of the formula calculates what the direct materials actually cost during the period.
Total variable manufacturing overhead variance
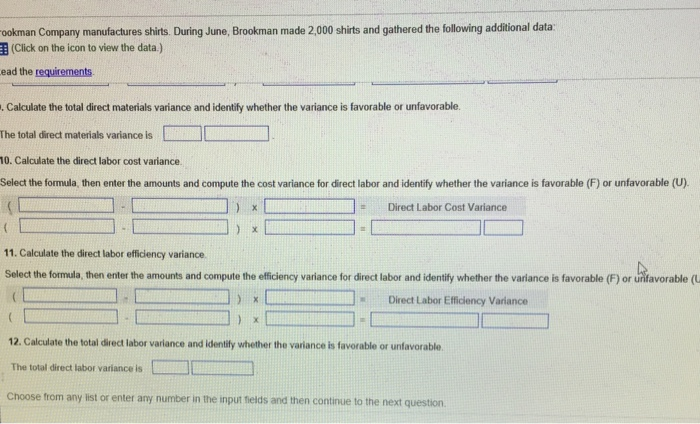
Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct labor variance template, compute the direct labor variances. Due to the higher than planned hourly rate, the organization paid $22,500 more for direct labor than they planned. This variance should be investigated to determine if the actual wages paid for direct labor can be lowered in future periods or if the standard direct labor rate per hour needs to be adjusted. For example, an investigation could reveal that the company had to pay a higher rate to attract employees, so the standard hourly direct labor rate needs to be adjusted.
The variable manufacturing overhead efficiency and rate variances are used to determine if the overall variance is an efficiency issue, rate issue, or both. A template to compute the total variable manufacturing overhead variance, variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance, and variable manufacturing overhead rate variance is provided in Exhibit 8-9. The fixed component of manufacturing overhead is comprised of overhead costs that stay the same in total regardless of the quantity produced or another cost driver. For example, rent expense for the production factory is the same every month regardless of how many units are produced in the factory. Within the relevant range of production, fixed costs do not have a quantity standard, only a price standard.
Practice Video Problem 8-3: Computing manufacturing overhead variances LO4
If more than \(600\) tablespoons of butter were used, management would investigate to determine why. Another element this company and others must consider is a direct materials quantity variance. Therefore, if the theater sells 300 bags of popcorn with two tablespoons of butter on each, the total amount of butter that should be used is 600 tablespoons. Management can then compare the predicted use of 600 tablespoons of butter to the actual amount used.
Standard costs variance analysis is used to determine the variances between the standard amounts projected for manufacturing costs and the actual amounts incurred. Any variance between the standard amounts allowed and actual amounts incurred should be investigated. The total price per unit variance is the standard price per unit of $0.50 less the actual price paid of $0.55 equals the price variance per unit of $(0.05) U. This is unfavorable because they actually spent more per unit than the standards allowed. The lock is lightweight, retractable, and fits easily in a jacket pocket.
In such cases, the responsibility of any unfavorable quantity variance would lie on the purchasing department. Irrespective of who appears to be responsible at first glance, the variance should be brought to the attention of concerned managers for quick and timely remedial actions. The standard price of materials purchased by Angro is $2.00 per kg and standard quantity of materials allowed to produce a unit of product is 1.5kg.
The total variances can be calculated in the last line of the top section of the template by subtracting the actual amounts from the standard amounts. The standard quantity allowed of 630,000 feet is subtracted from the actual quantity purchased and used of 600,000 feet, yielding a variance of 30,000 feet. Variances are favorable if the standard amount is more than the actual amount.
In this case, the actual quantity of materials used is \(0.20\) pounds, the standard price per unit of materials is \(\$7.00\), and the standard quantity used is \(0.25\) pounds. Like direct materials price variance, this variance may be favorable or unfavorable. On the other hand, if workers use the quantity that is more than the quantity allowed by standards, the variance is known as unfavorable direct materials quantity variance. Because the company uses 30,000 pounds of paper rather than the 28,000-pound standard, it loses an additional $20,700. To illustrate standard costs variance analysis for variable manufacturing overhead, refer to the data for NoTuggins in Exhibit 8-1 above.
To begin with, calculating direct material variance involves comparing the standard cost of materials to the actual cost incurred. This comparison helps businesses understand whether they are spending more or less than anticipated on raw materials. The standard cost is typically derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, or predetermined budgets, while the actual cost is recorded during the production process. This result is interpreted as the organization saved $15,000 in direct materials costs by using less direct material per unit than they planned. It is important to remember that standards are the planned or projected amounts.